Describe the Metabolic Response to Starvation
Alcohol consumption and energy metabolism 920. Starvation response in animals is a set of adaptive biochemical and physiological changes triggered by lack of food or extreme weight loss in which the body seeks to conserve energy by reducing the amount of calories it burns.

Undernutrition Simple And Stress Starvation
Glycogen - glucose under action of glucose-6-phosphatase.

. Our data capture this rise in. Additional MNT Considerations Short term starvation. METABOLIC STRESS STARVATION What is Metabolic Stress.
The metabolic responses to starvation and refeeding in adolescents with anorexia nervosa Ann N Y Acad Sci. Ketones are produced from fatty acids. Decline in metabolic rate Refeeding syndrome involves physiologic and metabolic.
During starvation most tissues utilise fatty acids andor ketone bodies to spare glucose for the brain. Metabolic responses to starvation 925. Coli upon glucose removal 21 22.
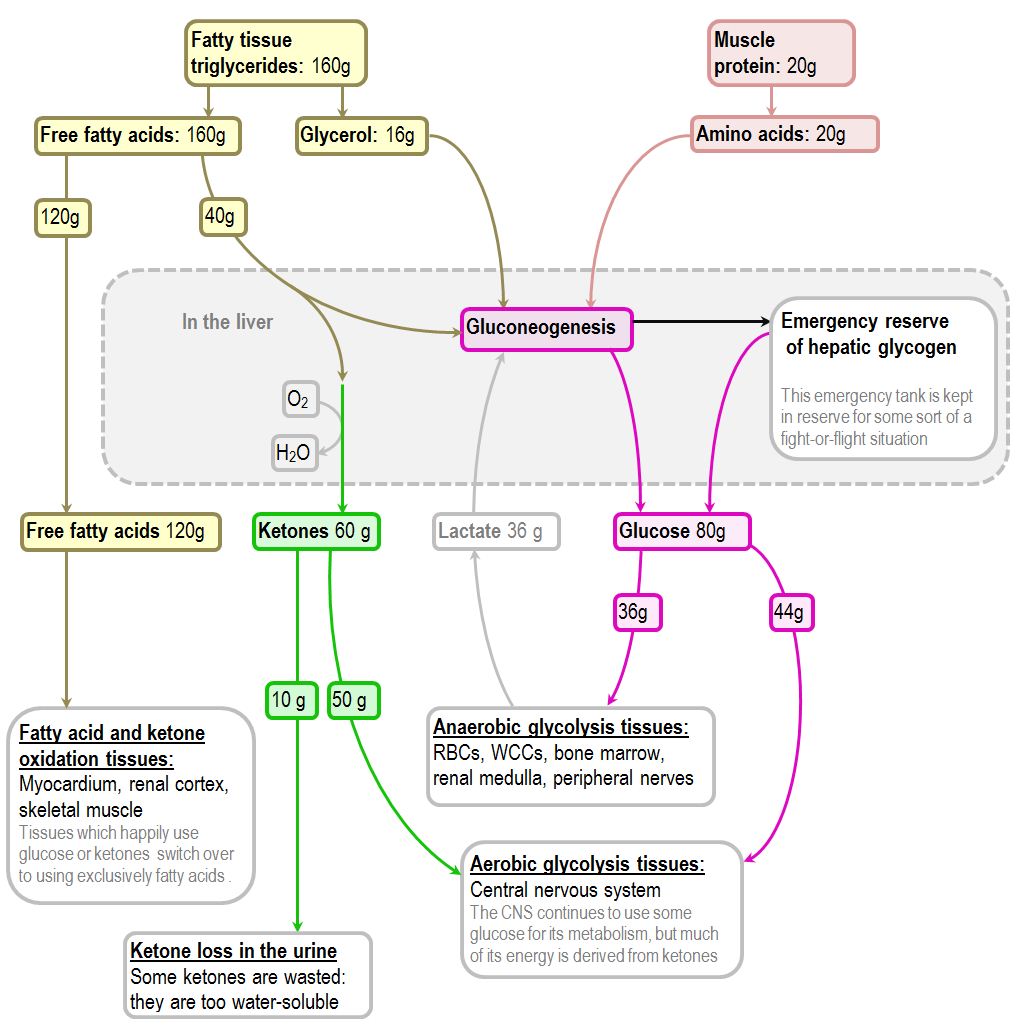
Initially stores of carbohydrate precursors eg. Characteristic Metabolic Responses to Carbon Starvation. Starvation Use of stored carbohydrate fat and protein to meet energy demands Liver glycogen Fatty acid stores Gluconeogenesis Glucose needed for brain and red blood cells Lean body mass protein and glycerol portion of triglycerides will be used instead.
Affiliation 1 Eating. Use of muscles for glucose in brain then fatty acid chains -- brain needs 100 grams of carbs ketone body production from fatty acid stores. Starvation for a long time will cause a metabolic shift in that our body uses fat as an energy source instead of glucose.
The metabolic response to prolonged starvation Early stage of prolonged starvation Starvation occurs when the body has a severe lack of nutrients needed to survive. The metabolic response to trauma in humans has been defined in 3 phases. Body uses stored energy as fuel when dietary intake.
Metabolic rate and the flexibility thereof is a complex trait involving several inter-linked variables that can influence animal energetics behavior and ultimately fitness. Briefly the human body response to starvation at a cellular level results in a reduced metabolic rate and a switching of food supply for various cells. Significantly from the responses of starved beetles kept at 12 C.
Glucose utilisation by the brain is decreased during prolonged starvation as the brain utilises ketone bodies as the major fuel. During starvation with no additional glucose available to the body glycogen stores glucose stores are consumed and then the. Beetles maintained at 20 and 24 C showed attributed to starvation resulting from the beetles inactivity almost the same responses when starved but differed caused by this low temperature.
Equivalent or closely related terms include famine response starvation mode famine mode starvation resistance starvation tolerance adapted. Energy Homeostasis in your body. Authors J E Schebendach 1 N H Golden M S Jacobson S Hertz I R Shenker.
Glycerol and gluconeogenic amino acids - glucose. Then in the first 24-48 hours there is increased gluconeogenesis from amino acids and glycerol. Bodys response to metabolic stress Nutrition Diagnoses What are possible nutrition diagnoses for metabolic stress.
Describe the metabolic response to starvation. Results obtained for the 16 C treatment indicated Metabolic responses over time in starved. Our methods are aimed at gaining a global view of metabolism.
Metabolic traits respond readily to ambient temperature variation in some cases increasing relative or. The metabolic response to starvation is characterised by a switch from carbohydrate metabolism to fat cmetabolism in. Starvation seriously alters the metabolic functions of our body.
Ebb phase or decreased metabolic rate in early shock phase Flow phase or catabolic phase Anabolic phase if the tissue loss can be replaced by re-synthesis once the metabolic response to trauma is stopped 9 10. Decreased insulin increased glucagon - increased hepatic glycogenolysis gluconeogenesis amino acid uptake ureagenesis protein catabolism. High concentrations of ketone bodies result in significant excretion of ketones.
Metabolic responses to exercise 832. The body has ways of adapting to periods without food for example overnight it needs to survive without any additional nutrients whilst asleep. Stress and energy metabolism 904.
Metabolic responses to starvation and feeding contribute to the invasiveness of an emerging pest insect. Glucose is a primary cellular food source used by all cells in the body. The human body switches from burning carbohydrates to fat to maintain the blood glucose levelAt the time of starvation the plasma level of fatty acids and ketone bodies.
Among the best established of these is increased cAMP in E. An important test of the validity of our approach is its ability to recapitulate literature findings on specific compounds.
Physiological Adaptation To Prolonged Starvation Deranged Physiology


No comments for "Describe the Metabolic Response to Starvation"
Post a Comment